Sunday, April 12th
Happy Easter Sunday!! I hope you have all had a great week and have stayed safe and healthy. This week I have decided to focus on COVID-19 again. More and more recently I have read and heard on the news about an antibody responses for the virus and it was very interesting to me. In my Microbiology class we have been discussing antibodies, so I thought this topic would be perfect for this week.
Quick Review of Antibodies
Before I dive into the antibody responses for COVID-19, it is important that I explain what an antibody response is. An antibody is a protein produced by your body’s immune system in response to a specific pathogen. After they are produced they circulate the body looking for the pathogen they are specific for. It takes about two weeks (10 to 14 days) for the immune system to secrete a significant number of antibodies to be able to effectively inhibit the pathogen and to kill it. Further, the antibodies will last in the blood after the pathogen is eradicated. There are many actions which antibodies can do to kill pathogen or the infected human cell. There are five classes of antibodies, which include: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, and IgE. These antibodies differ in their immune response effects, as well the differ in when they are produced throughout a primary and secondary immune response.
The two important ones pertaining to the coronavirus are IgG and IgM. The IgM antibody is the “fast reaction” antibody. This antibody is produced relatively quickly by the body in order to activate an immune response the invading pathogen (in this case the coronavirus). On the other hand, the IgG antibody takes longer to get activated, but is more powerful in its attack. This antibody is better able to target the pathogen and keeps the body safe afterward. The following is a graph which highlights the concentrations of IgG and IgM antibodies through and after a primary and secondary infection.
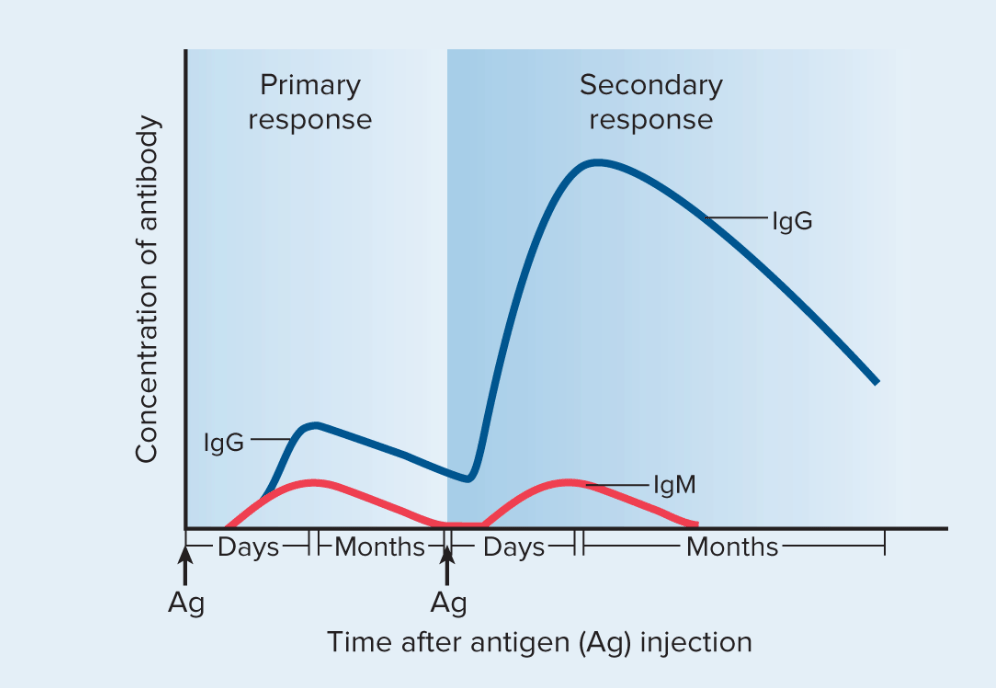
Antibody Testing with COVID-19
At the beginning of April, the FDA approved the first antibody test in the United States, under the biotech company Cellex. The type of test which looks at one’s antibodies is called a serological test. With this type of test the medical professional will draw blood from the person’s veins where it will then be analyzed in a lab. Specifically, the type and concentrations of antibodies will be assessed. With coronavirus, the concentrations of IgM and IgG are observed.
When analyzing the patient’s blood, if the medical profession finds only IgM antibodies in their blood, it suggests that they are within the early days of infection with the virus. As stated above, IgM is the antibody produced first as a means to jump start the immune system until the more effective antibodies are produced. So when this antibody is found in significant concentrations, without others, it shows that the immune system has not had enough time to produce the more effective antibodies, like IgG. The presence of both IgM and IgG antibody will reflect that the person is either in the later stages of fighting the infection or beginning stages of recovery. As the immune response progresses, it will start to make less IgM and more of the efficient antibodies, like IgG. IgG levels will still remain high even after the infection has been cleared from the body. If the blood sample has primarily IgG titers, then that person has recovered from the virus, and now has some protection to it. It is with these results that they are unable to infect people, as their immune system has effective eradicated the virus, and thus they are no longer infectious.
This antibody tests created by Cellex is an amazing advancement in our efforts to help find treatment and a cure for the coronavirus. First off, you get the test results within 15 to 20 minutes after they draw your blood. Further, this test will shed a lot more light on how many people have mild/ asymptomatic infections from this virus. This will help researchers and scientist get a better understanding of COVID-19 and the affect on our population.
Prior to this the diagnostic test used widely was the PCR test. With this test you take a swab and stick it up their nasal cavity all the way to their nasopharynx . This sample will get sent to a lab, where it is analyzed. The medical professional will be looking for RNA fragments from the coronavirus. This test can only conclude if someone is currently infected with the virus. I have seen videos of people receiving these test, and boy do they look painful! Additionally, these test typically take days to figure out the results.
It is important to have antibody tests because unlike the nasal swap (PCR) test, the antibody test will tell someone if they have or have had coronavirus, and if they are recovered. This will help researchers and scientist have a better understanding of how many people have had this virus. It will also give them better data on people with mild and asymptomatic cases. I think that it is important to know this knowledge because the more we know this the better and more accurate our data can be, which will only help them in their efforts for a cure.
—–
I hope you all enjoyed this weeks blog! I think that it is very salient to understand the body’s antibody response to this virus, because it will help in the efforts for creating an effective vaccine. To create an effective vaccine, it will need to mimic the body’s natural response to the virus in order to create a proper immune response to it. I hope the FDA starts approving more antibody tests so that we can have a better and more efficient system of testing people. I hope this will happen so we can get back to some semblance of “normal” as soon as possible. But, more importantly I hope these tests will give researchers and scientist more knowledge about this virus so that they can make an effective vaccine and treatments. I hope you all have a great week and look out for next weeks blog!